- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
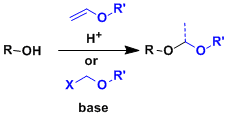
Alcohols can be protected as acetals against reductive and basic conditions. Oxygen-based acetals are also stable under oxidizing conditions. Deprotection is usually done under acidic conditions.
-
General References
・Bennech, T. Synthesis 1995, 1. DOI: 10.1055/s-1995-3858
-
Examples
THP protection/deprotection catalyzed by iodine. [1]

-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
Typical acetals used to protect alcohols are as follows.
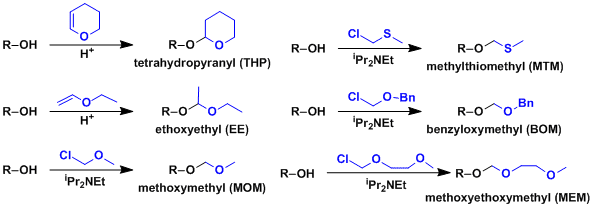
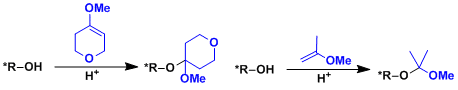
THP and EE are easy ones to put on but have a downside that they give rise to diastereomers when the alcohol is chiral, which could make the analysis complex. Protection using either 5,6-dihydro-4-methoxy-2H-pyran or 2-methoxypropene can avoid the problem.
MOM is relatively stable and its deprotection requires TFA or dilute HCl. Orthogonal deprotection of MEM, BOM, and MTM against MOM can be effected by chelating Lewis acids (e.g. ZnBr2), reduction, and soft Lewis acids (e.g. Hg), respectively.
-
References
[1] Kumar, H. M. S.; Reddy, B. V. S.; Reddy, E. J.; Yadav, J. S. Chem. Lett. 1999, 857. doi:10.1246/cl.1999.857
-
Related Books
[amazonjs asin=”0471697540″ locale=”US” title=”Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis”]
[amazonjs asin=”1588903761″ locale=”US” title=”Protecting Groups (softcover)”]