- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
-Benzyl group (Bn) is stable towards both acids and bases and is a highly general protecting group.
-Base sensitive compounds can be protected using BnOC(=NH)CCl3 under acidic conditions.
-Deprotection is usually done under reductive conditions (H2-Pd/C, Na/NH3(l), electrolytic reduction, etc). Alternatively, benzyl groups can be deprotected by RuCl3/NaIO4 oxidation-then-hydrolysis or by the combination of a Lewis acid and a nucleophile (such as Me2BBr).
-
General References
・Czernecki, S.; Georgoulis, C.; Provelenghiou, C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976, 17, 3535. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)71351-7
・White, J. D.; Reddy, G. N.; Spessard, G. O. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1624. DOI: 10.1021/ja00213a047
-
Reaction Mechanism
1. Protection
Follows the mechanism of Williamson ether synthesis.
![PG_Bn_2[1]](https://assets.en.chem-station.com/uploads/2014/03/PG_Bn_21.gif) 2. Deprotection (reductive conditions)
2. Deprotection (reductive conditions)
-
Examples
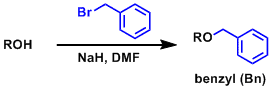
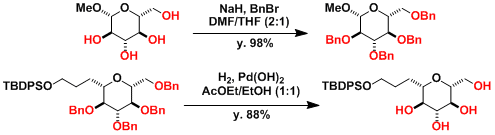
Typical protection and deprotection examples[1]: Benzyl group is stable, therefore protection is often done during the early stage of syntheses.
Selective cleavage of N-Bn in the presence of O-Bn is possible.[2]
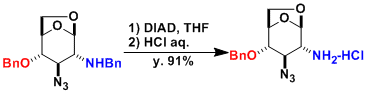
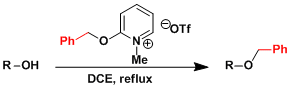
The Dudley reagent[3]: This bench stable reagent is easy to handle and capable of benzylation under nearly neutral conditions.
-
Experimental Procedure
-The substrate is reacted with BnCl or BnBr in DMF with NaH as a base. Benzylated products are generally obtained in high yield.
-The catalytic addition of Bu4NI (TBAI) or NaI accelerates benzylation (through in situ formation of reactive BnI).
-
Experimental Tips
-Benzyl bromide is a lachrymator. Handle it inside a fume hood.
-Quenching the reaction with methanol/potassium carbonate instead of water is a nice way to destroy unreacted benzyl bromide. This procedure is recommended as it makes extraction easier.
-
References
[1] Oguri, H.; Hishiyama, S.; Oishi, T.; Hirama, M. Synlett 1995, 1252. DOI: 10.1055/s-1995-5259
[2] Kroutil, J.; Tmka, T.; Cemy, M. Synthesis 2004, 446. DOI: 10.1055/s-2004-815937
[3] (a) Poon, K. W. C.; Dudley, G. B. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 3923. DOI: 10.1021/jo0602773 (b) Poon, K. W. C.; House, S. E.; Dudley, G. B. Synlett 2005, 3142. DOI: 10.1055/s-2005-921898
-
Related Books
[amazonjs asin=”0471697540″ locale=”US” title=”Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis”]
[amazonjs asin=”0865779937″ locale=”US” title=”Protecting Groups (Foundations of Organic Chemistry)”]
[amazonjs asin=”0198502753″ locale=”US” title=”Protecting Group Chemistry (Oxford Chemistry Primers)”]