- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
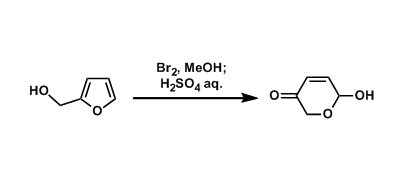
Under oxidative conditions, furfuryl alcohol can be converted into dihydropyran. Reagents such as bromine, NBS, and mCPBA are used commonly to effect this type of transformation. In a sense, the furan ring can be viewed as a precursor of 1,4-dicarbonyl compounds.
-
General References
- Achmatowicz, O.; Bukowski, P.; Szechner, B.; Zwierzchowska, Z.; Zamojski, A. Tetrahedron 1971, 27, 1973. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98229-8
<reviews>
- Ciufolini, M. A.; Hermann, C. Y. W.; Dong, Q.; Shimizu, T.; Swaminathan, S.; Xi, N. Synlett 1998, 105. DOI: 10.1055/s-1998-1584
- Harris, J. M.; Li, M.; Scott, J. G.; O’Doherty, G. A. in Strategy and Tactics in Natural Product Synthesis, ed. M. Harmata, Elsevier, London, 2004, 5, 221–253.
- Merino, P. Curr. Org. Chem. 2007, 11, 1076.
-
History
In 1971, a Polish chemist Osman Achmatowicz Jr. reported a procedure to synthesize monosaccharides by treating furfuryl alcohol with bromine. This and related reactions are called the Achmatowicz reaction after his name.
-
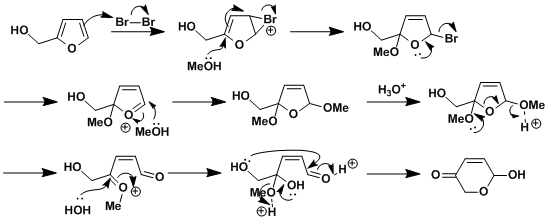
Reaction Mechanism
-
Examples
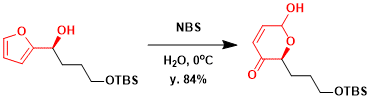
A high yielding example in the synthesis of D-swainsonine.[1]
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] Guo,H.; O’Doherty, G. A. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1609. DOI: 10.1021/ol0602811
-
Related Books
[amazonjs asin=”0124171850″ locale=”US” title=”Strategies and Tactics in Organic Synthesis, Volume 10″]
-
External Links
Achmatowicz Reaction (Chemical Christallintiy)