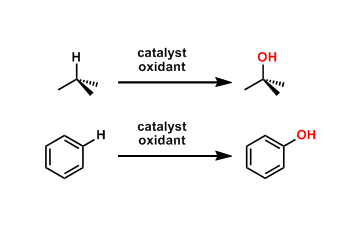
General Characteristics Catalytic C-H oxidation is a type of C-H activation reactions by which one can oxygenate unreactive C-H bonds, which are present ubiquitously in organic compounds. The C-H ...
Monthly Archives: April 2015
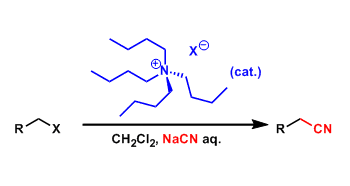
Phase-Transfer Catalyst (PTC)
General Characteristics Reactions such as SN2 substitution involve deprotonation by strong bases and combining the resulting anions with electrophiles. These reactions often necessitate the use of ...
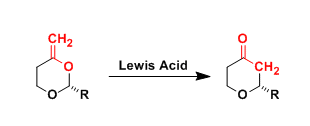
Petasis-Ferrier Rearrangement
General Characteristics The Lewis acid-promoted rearrangement of enol acetals to cyclic ethers, which involves an oxygen-to-carbon transposition, is known as the Petasis-Ferrier rearrangement. This ...
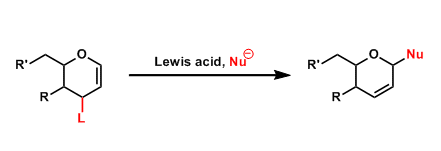
Ferrier Rearrangement
General Characteristics The introduction of nucleophilic groups to the 1-position of 1,2-glycals by an allylic substitution is called the Ferrier reaction. This reaction is referred to as the “Type ...
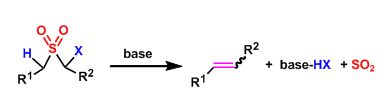
Ramberg-Backlund Rearrangement
General Characteristics The basic treatment of α-halogenated sulfones leads to the formation of alkenes with the elimination of sulfur dioxide. This reaction is called the Ramberg-Backlund reaction ...
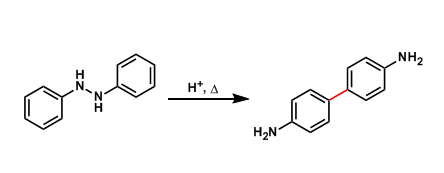
Benzidine Rearrangement
General Characteristics Under acidic conditions, 1,2-diphenylhydrazines are known to rearrange into 4,4’-diaminobiphenyls (benzidines). General References Hofmann, A. W. Proc. Roy. Soc. London ...
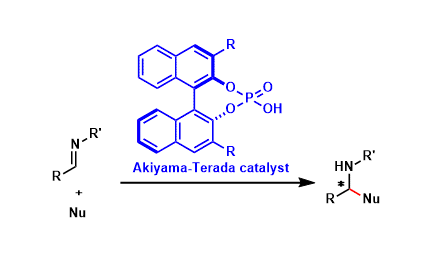
Akiyama-Terada Catalyst
General Characteristics The phosphoric acids containing an appropriately substituted BINOL backbone function as chiral Brønsted acid catalysts that can promote a wide range of stereoselective ...
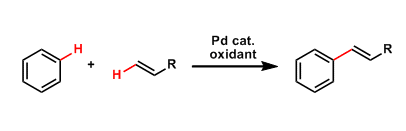
Fujiwara-Moritani Reaction
General Characteristics The direct coupling between unsubstituted aromatic rings and olefins in the presence of palladium catalysts is called the Fujiwara-Moritani reaction. This reaction is one of ...