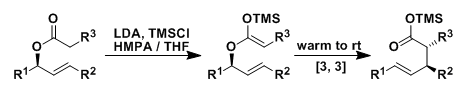
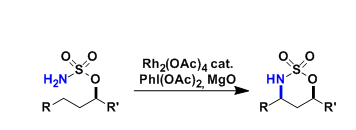General Characteristics The Ireland-Claisen rearrangement is a version of the Claisen rearrangement in which ketene silyl acetals (prepared from allyl esters) undergo [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement ...
Monthly Archives: March 2015
Overman Rearrangement
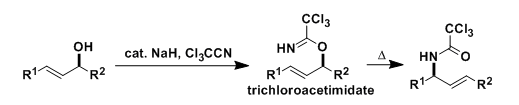
General Characteristics The trichloroacetimidates of allylic alcohols, prepared using trichloroacetonitrile, undergo thermal or catalyzed [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement, which is referred to as the ...
Aza-Cope Rearrangement
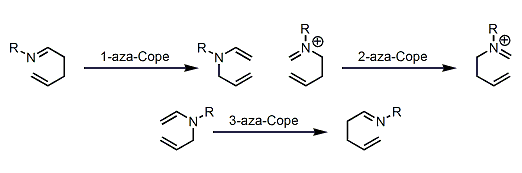
General Characteristics Nitrogen-containing 1,5-dienes undergo [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement just like the Cope rearrangement of 1,5-dienes. Among these so-called aza-Cope rearrangements, the 3-aza ...
Diazomethane
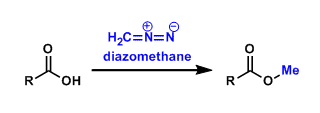
General Characteristics Diazomethane (CH2N2) is the simplest example of diazo compounds. It is traditionally used to synthesize methyl esters of carboxylic acids. This methyl ester formation is very ...
Du Bois Amination
General Characteristics The direct amination of unactivated C-H bonds utilizing metal nitrenoids, especially with Rh-catalysis, became a practical synthetic option in the early 2000’s. This reaction ...
Cyclopropanation with Metal Carbenoids
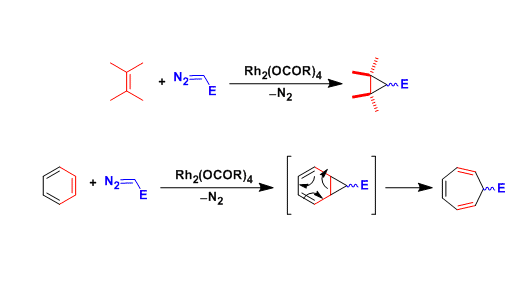
General Characteristics In the presence of metal catalysts, diazo compounds decompose to generate metal carbenoid species, which react with olefins to give cyclopropanes. Metal carbenoids also react ...
Achmatowicz Reaction
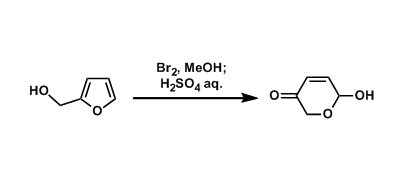
General Characteristics Under oxidative conditions, furfuryl alcohol can be converted into dihydropyran. Reagents such as bromine, NBS, and mCPBA are used commonly to effect this type of ...
Sugasawa Reaction
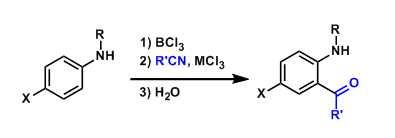
General Characteristics The ortho-acylation of unprotected anilines using nitriles is known as the Sugasawa reaction. The Friedel-Crafts acylation of anilines is inherently difficult because the ...
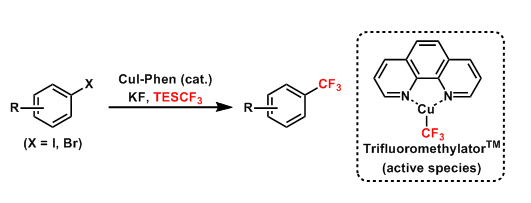
Amii Trifluoromethylation
General Characteristics Aromatic halides can be trifluoromethylated by copper-catalyzed cross coupling developed by Amii. This procedure is applicable to the introduction of other perfluoroalkyl ...
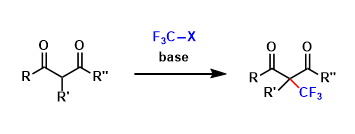
Electrophilic Trifluoromethylation
General Characteristics Fluorine and hydrogen are about the same size, but are electronically very different. The substitution of hydrogen atoms with fluorine atoms is a common way of tuning the ...