- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
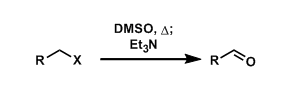
Alkyl halides can be converted into the corresponding aldehydes by thermally driven displacement by DMSO followed by treatment with bases.
-
General References
・Kornblum, N.; Jones, W. J.; Anderson, G. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 4113. DOI: 10.1021/ja01524a080
・Kornblum, N.; Jones, W. J.; Anderson, G. J.; Powers, J. W.; Larson, H. O.; Levand, O.; Wraver, W. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 6562. DOI: 10.1021/ja01581a057
・Dave, P.; Byun, H. S.; Engel, R. Synth. Commun. 1986, 16, 1343.
-
Reaction Mechanism
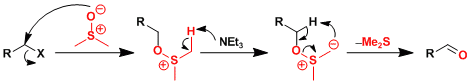
The reaction mechanism is analogous to other DMSO-based oxidation reactions, and thus an equivalent of dimethylsulfide is produced as byproduct.
-
Examples
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
-
Related Reactions
アルブライト・ゴールドマン酸化 Albright-Goldman Oxidation
パリック・デーリング酸化 Parikh-Doering Oxidation
フィッツナー・モファット酸化 Pfitzner-Moffatt Oxidation
-
Related Books
-
External Links
Oxidations (PDF)
Kornblum Oxidation – Wikipedia