- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
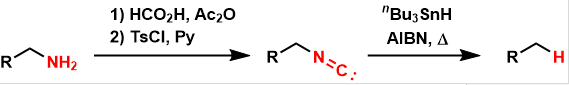
In the Barton deamination, amines are converted to isonitriles and then reductively removed under free-radical conditions, yielding simple hydrocarbons.
-
General References
Barton, D. H. R. et al. Aldrichimica Acta 1990, 23, 3.
-
Reaction Mechanism
-
Examples
Synthesis of octadecane from the corresponding isonitrile.[1]

A solution of the isocyanide (0.279 g) and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) (0.1 g) in dry xylene (50 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of tri-n-butylstannane (0.64 g, 2.2 mol equiv.) in refluxing xylene (50 mL), under nitrogen, over 2 h. A solution of AIBN (0.1 g) in xylene (50 mL) was slowly added over 5 h. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue dissolved in pentane. Iodine in pentane solution was added until the colour of iodine persisted. The solvent was removed and the octadecane was isolated by preparative t.l.c. (SiO2, pentane) and sublimation in vacuo (0.205 g, 81%, m.p. 29 ºC).
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] Barton, D. H. R. et al. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1980, 2657.
-
Related Reactions
-
Related Books
-
External Links
- Derek Harold Richard Barton (Wikipedia)
- Barton Reaction