-
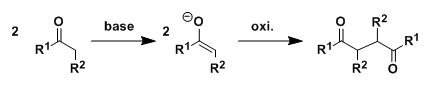
General Characteristics
Enolate species undergo dimerization under appropriately chosen oxidative conditions. Homo-coupling usually predominates, but there are successful examples of controlled hetero-coupling using carefully designed substrates.
-
General References
-
Reaction Mechanism
-
Examples
In 2007, MacMillan reported the remarkable catalytic enantioselective version of enolate coupling, the reactivity of which has been explained by SOMO (singly occupied molecular orbital)-activation mechanism.[1]
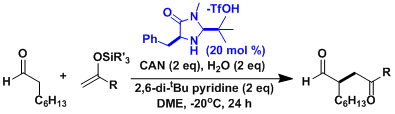
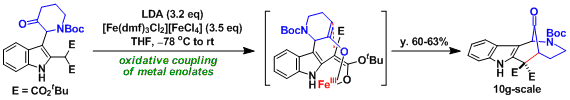
The application in the context of actinophyllic acid total synthesis.[2]
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] Jang, H.-Y.; Hong, J. B.; MacMillan, D. W. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7004. DOI: 10.1021/ja0719428 [2] Martin, C. L.; Overman, L. E.; Rohde, J. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7568. doi: 10.1021/ja803158y
-
Related Reactions
-
Related Books
-
External Links