- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
Synthetically important aryl and alkenyl boron compounds can be synthesized from the corresponding halides via transition metal catalysis. Bis(pinacolato)diboron is used commonly as the boron source due to stability, easy handling, and wide commercial availability.
In the past dacade, iridium- and rhodium-catalyzed efficient direct C-H borylation reactions that do not require halogenated precursors have been reported.
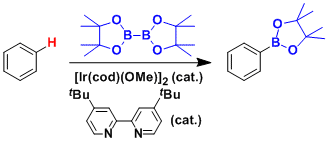
The iridium-catalyzed systems are sensitive to steric influences and allow for meta-functionalization, which is difficult by conventional lithiation and electrophilic substitution approaches.
-
General References
・Ishiyama, T.; Murata, M.; Miyaura, N. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 7508. DOI: 10.1021/jo00128a024
・Ishiyama, T.; Takagi, J.; Ishida, K.; Miyaura, N.; Anastasi, N. R.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124,
390. DOI: 10.1021/ja0173019
・Takagi, J.; Takahashi, K.; Ishiyama, T.; Miyaura, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8001. DOI: 10.1021/ja0202255
・Ishiyama, T.; Takagi, J.; Hartwig, J. F.; Miyaura, N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3056. [abstract]
-
Reaction Mechanism
-
Examples
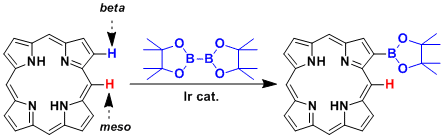
The β-selective C-H borylation of porphyrin.
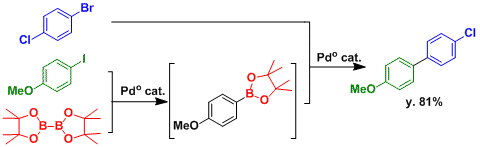
By selecting substrates with appropriate reactivity, the sequential Miyaura borylation-then-Suzuki-Miyaura cross coupling can be achieved.
The rhodium-catalyzed functionalization of unreactive alkanes at terminal position.[1]
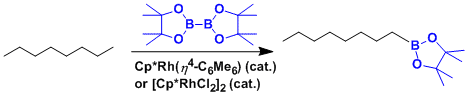
-
Experimental Procedure
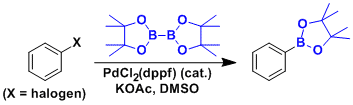
Borylation of aryl bromide.[2]
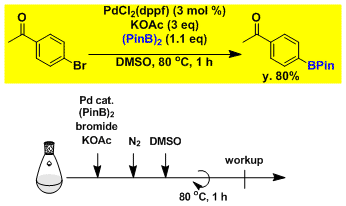
-
Experimental Tips
KOAc is the base of choice. Stronger bases like K2CO3 and K3PO4 increases the risk of dimerization via the Suzuki coupling.
The order of reaction rate in different solvents is: DMSO >> DMF > 1,4-dioxane.
-
References
[1] Chen, H.; Schlecht, S.; Semple, T. C.; Hartwig, J. F. Science 2000, 287, 1995. doi:10.1126/science.287.5460.1995
[2] Ishiyama, T.; Murata, M.; Miyaura, N. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 7508. DOI: 10.1021/jo00128a024
-
Related Books