- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
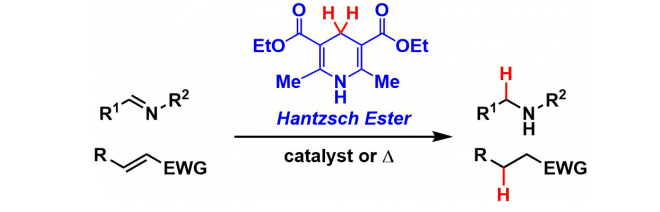
Dihydropyridine (Diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate) synthesized from formaldehyde and ethyl acetoacetate is commonly called the Hantzsch ester.
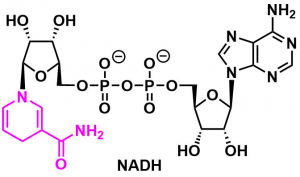
The Hantzsch ester is used as a hydride donor reagent in reduction reactions, often with organocatalysts or photo-redox catalysts. It can be regarded as the chemical analogue of NADH (the biological reductant), since they share the dihydropyridine active structure.
-
General References
- Norcross, B. E., Klinedinst, Jr., P. E., Westheimer, F. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 797. DOI: 10.1021/ja00864a024
- Singh, S.; Sharma, V. K.; Gill, S.; Sahota, R. I. K. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1. 1985, 437. DOI: 10.1039/P19850000437
<Reviews>
- Torchy, S.; Cordonnier, G.; Barbry, D.; Eynde, J. J. V. Molecules 2002, 7, 528. doi:10.3390/70700528
- Connon, S. J. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 3407. DOI: 10.1039/B711499K
- de Vries, J. G.; Mrsic, N. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 727. DOI: 10.1039/C1CY00050K
- Rueping, M.; Dufour, J.; Schoepke, F. R. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1084. DOI: 10.1039/C1GC15027H
- Zheng, C.; You, S.-L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2498. DOI: 10.1039/C1CS15268H
- McSkimming, A.; Colbran, S. B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5439. DOI: 10.1039/C3CS35466K
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6621. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00203
-
Reaction Mechanism
-
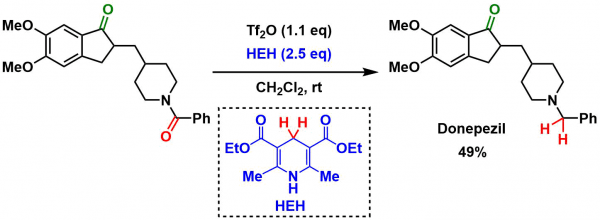
Examples
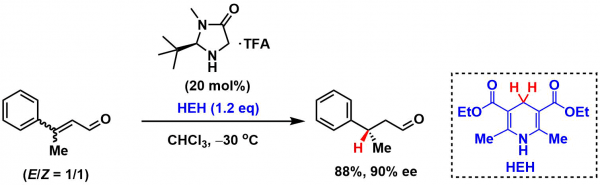
Asymmetric conjugate reduction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes with Hantzsh ester catalyzed by MacMillan’s imidazolidinone catalyst.[1]
Metal-free and chemoselective reduction of amide.[2]
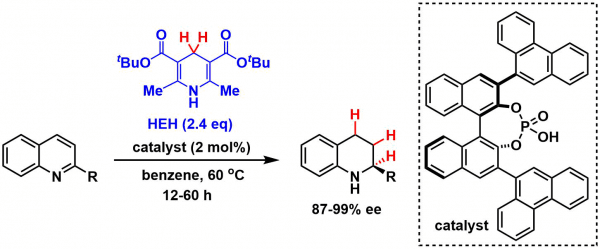
Asymmetric reduction of quinolines catalyzed by the Terada-Akiyama phosphoric acid catalyst.[3]
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
- Ouellet, S. G.; Tuttle, J. B.; MacMillan, D. W. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 128, 32. DOI: 10.1021/ja043834g
- (a) Barbe, G.; Charette, A. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 18. DOI: 10.1021/ja077463q (b) Improvement with Et3SiH: Pelletier, G.; Bechara, W. S.; Charette, A. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12817. DOI: 10.1021/ja105194s
- Rueping, M.; Theissmann, T. Chem. Sci. 2010, 1, 473. DOI: 10.1039/C0SC00206B
-
Related Reactions
-
Related Books
[amazonjs asin=”0412381508″ locale=”US” title=”Heterocyclic chemistry: 2nd edition”]
-
External Links
- Structure, Mechanism and Reactivity of Hantzsch Esters (MacMillan’s group, PDF)
- Hantzsch Ester (organic-chemistry.org)