Overall Score4
- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
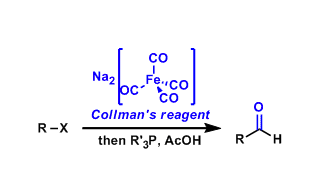
Disodium tetracarbonylferrate is generally referred to as the Collman reagent. It reacts with alkyl halides to give corresponding aldehydes and ketones.
-
General References
- Collman, J. P.; Winter, S. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 4089. DOI: 10.1021/ja00793a066
- Collman, J. P.; Finke, R. G.; Cawse, J. N.; Brauman, J. I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 2515. DOI: 10.1021/ja00450a019
- Collman, J. P. Acc. Chem. Res. 1975, 8, 342. DOI: 10.1021/ar50094a004
-
History
Na2[Fe(CO)4] complex and its synthetic applications were reported by James Collman in the 1970’s.
-
Reaction Mechanism
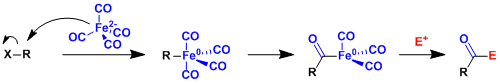
-
Examples
Unsymmetrical ketones can be synthesized by reacting two benzyl halides with the Collman’s reagent sequentially.[1]

-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] Potter, R. G.; Hughes, T. S. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 1187. DOI: 10.1021/ol0629770
-
Related Reactions
-
Related Books
[amazonjs asin=”189138953X” locale=”US” title=”Organotransition Metal Chemistry: From Bonding to Catalysis”]
-
External Links

![2014-10-05_01-21-02[1]](https://assets.en.chem-station.com/uploads/2015/06/2014-10-05_01-21-021.png)