- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
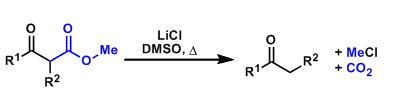
β-Keto methyl esters undergo decarboxylation under near neutral conditions upon heating in the presence of lithium chloride in DMSO. This reaction is particularly useful when the compound that needs to be decarboxylated is base-sensitive.
-
General References
Krapcho, A. P.; Glynn, G. A.; Grenon, B. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967, 8, 215. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)90519-7
Krapcho, A. P.; Jahngen, E. G. E.; Lovey, A. J.; Short, F. W. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15, 1091. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82414-X
Krapcho, A. P.; Weimaster, J. F.; Eldridge, J. M.; Jahngen, E. G. E.; Lovey, A. J.; Stephens, W. P. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 138. doi:10.1021/jo00395a032
Review: Krapcho, A. P. Synthesis 1982, 805. DOI: 10.1055/s-1982-29953
Review: Krapcho, A. P. Synthesis 1982, 893. DOI: 10.1055/s-1982-29991
-
Reaction Mechanism
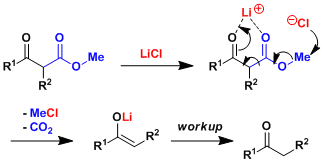
The lithium ion acts as a Lewis acid to activate the β-ketoester and the nucleophilic attack by the chloride triggers the decarboxylation. (Ref: Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 3929.)
-
Examples
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
-
Related Reactions
Acetoacetic Ester / Malonic Ester Synthesis
-
Related Books
-
External Links