- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
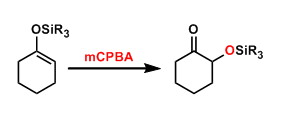
The epoxidation of silyl enol ethers with oxidants such as mCPBA and dioxirane leads to rearrangement into α-silyloxyketones. This reaction is used commonly to introduce a hydroxyl group to the α-position of ketones.
-
General References
・ Rubottom, G. M.; Vazquez, M. A.; Pelegrina, D. R. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15, 4319. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)92153-7
・ Brook, A. G.; Macrae, D. M. J. Organomet. Chem. 1974, 77, C19. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)81332-7
・ Hassner, A.; Reuss, R. H.; Pinnick, H. W. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 3427. DOI: 10.1021/jo00911a027
-
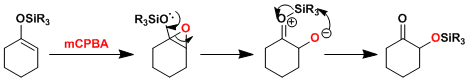
Reaction Mechanism
-
Examples
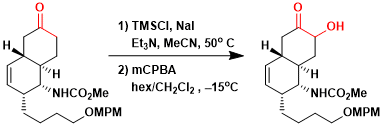
The regioselective α-hydroxylation of a complex ketone in the synthesis of (-)-stenine.[1]
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] Morimoto, Y.; Iwahashi, M.; Nishida, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Shirahama, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1996, 35, 904. DOI: 10.1002/anie.199609041
-
Related Reactions
- Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
- dimethyldioxirane
- Jacobsen-Katsuki Epoxidation
- Davis Oxidation
- Prilezhaev Epoxidation
- Saegusa-Ito Oxidation
-
Related Books
-
External Links
- Oxidation (A.Myers’ Lab.: PDF)
- Rubottom Oxidation (organic-chemistry.org)
- Rubottom Oxidation (Wikipedia)