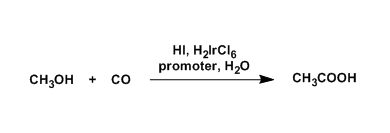Overall Score4.5
- Industrial Importance
- Scale Up of Catalytic Chemistry
- Criteria #3
- Criteria #4
- Criteria #5
-
General Characteristics
Acetic acid is produced in different ways, such as by carbonylation of methanol and oxidation of acetaldehyde or hydrocarbons. The two carbonylation processes, the rhodium-catalyzed Monsanto process and the iridium-catalyzed Cativa process, are used to supply 60% of all acetic acid in the world.
-
General References
Sunley, G. J.; Watson, D. J. Catalysis Today, 2000, 58, 293. DOI:10.1016/S0920-5861(00)00263-7
-
Reaction Mechanism
The catalytic cycle is fundamentally similar to the Monsanto process.
Adding an inexpensive promotor increases the catalytic efficiency. The promotor is thought to scavenge iodide ions and create a coordination site for CO, facilitating the migratory insertion step. (Ref: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2847.)
-
Examples
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
-
Related Reactions
Monsanto Process for Acetic Acid Synthesis
-
Related Books
-
External Links