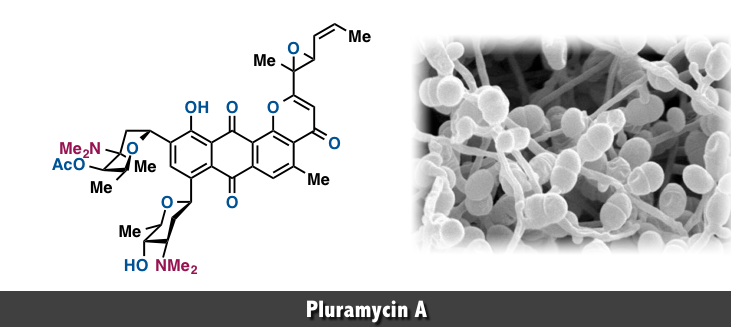
The pluramycin family of natural products are an important group of complex C-aryl glycoside antibiotics that possess the tetracyclic 4H-anthra[1,2-b]pyran-4,7,12-trione moiety A–D as an aromatic core. The D-ring is adorned with two deoxyaminosugars that are appended by C-aryl glycosidic linkages. The E-ring sugar is angolosamine, a carbohydrate that is also found in the antibiotic angolamycin The F-ring sugar is the N,N-dimethyl derivative of vancosamine, which is the sugar found in the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin.
These compounds exhibit potent antitumor activity by DNA alkylation, where the two proximal amino sugars, D-angolosamine and N,N-dimethyl-L-vancosamine, play a key role in sequence recognition in intercalation of the tetracyclic chromophore.[1]
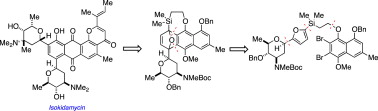
In 2010, Martin and coworkers report the first total synthesis of the complex C-aryl glycoside isokidamycin, the epimer of the naturally-occurring pluramycin antibiotic kidamycin.[2] In 2013, Prof. Keisuke Suzuki, Tokyo Institute of Technology has achieved a concise, highly convergent total synthesis of saptomycin B, a member of the pluramycin class of antitumor antibiotics.[3]
-
References
[1] For reviews, see: (a) Hansen, M. R.; Hurley, L. H. Acc. Chem. Res. 1996, 29, 249. DOI: 10.1021/ar950167a (b) Willis, B.; Arya, D. P. Curr.
Org. Chem. 2006, 10, 663. DOI: 10.2174/138527206776359739
[2] “Studies toward the syntheses of pluramycin natural products. The first total synthesis of isokidamycin ”
We report the first total synthesis of the complex C-aryl glycoside isokidamycin, the epimer of the naturally-occurring pluramycin antibiotic kidamycin. The synthesis features a highly efficient Diels–Alder reaction between a substituted naphthyne and a glycosylated furan to form the anthracene core bearing a pendent angolosamine C-glycoside. The regiochemical outcome of the Diels–Alder reaction was controlled by employing a disposable silicon tether to link the reactive naphthyne and the glycosyl furan, rendering the cycloaddition intramolecular. The benzopyranone moiety of the aromatic nucleus was appended by cyclization of a functionalized vinylogous amide onto an advanced anthrol intermediate. The vancosamine amino glycoside was introduced by an O→C-glycoside rearrangement that produced the β-anomer. Subsequent refunctionalizations then led to isokidamycin.
[3] “Synthesis of the Pluramycins 2: Total Synthesis and Structure Assignment of Saptomycin B”
Kitamura, K.; Maezawa, Y.; Ando, Y. Angew. Chem. 2014. Early view. DOI:10.1002/anie.201308017
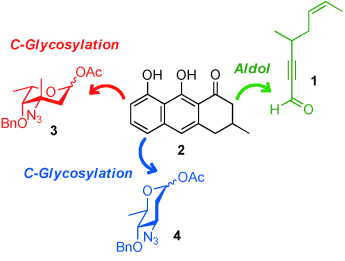
A concise, highly convergent total synthesis of saptomycin B, a member of the pluramycin class of antitumor antibiotics, is reported. The target compound was assembled from four building blocks (a tricyclic platform, two sugars, and an alkynal) in 15% yield through 10 synthetic operations. The key steps included the regioselective installation of two amino sugars (l-vancosamine and d-angolosamine) on the tricycle and the efficient construction of the tetracyclic skeleton by an aldol reaction followed by formation of the pyranone. The unknown configuration at C14 was assigned as R.
-
Related Books
[amazonjs asin=”1588293831″ locale=”US” title=”Natural Products: Drug Discovery and Therapeutic Medicine”]