Robertson, A. P. M.; Burford, N.; McDonald, R.; Ferguson, M. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 2014. Early View.
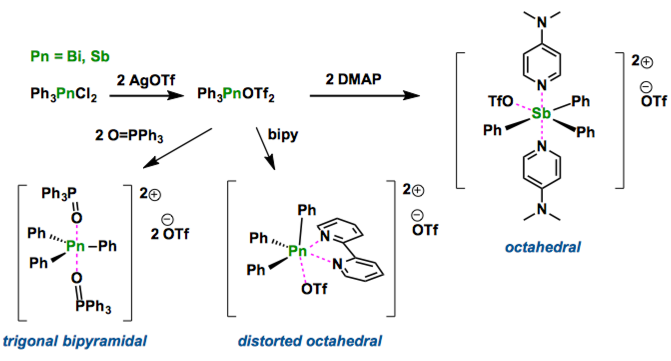
The syntheses of salts containing ligand-stabilized Ph3Sb2+ and Ph3Bi2+ dications have been realized by in situ formation of Ph3Pn(OTf)2 (Pn=Sb or Bi) and subsequent reaction with OPPh3, dmap and bipy. The solid-state structures demonstrate diversity imposed by the steric demands and nature of the ligands. The synthetic method has the potential for broad application enabling widespread development of the coordination chemistry for Pn(V) acceptors.
Recent development of bismuth chemistry is dramatic. As bismuth compounds are found to be non-toxic, and relatively inexpensive, their applications have been paid a considerable attention.[1] In fact, several bismuth compounds show the catalytic activity in organic synthesis such as allylation of aldehyde, and commonly the neutral or mono-cationic bismuth derivatives are used. In this report, Burford group synthesized the dicationic bismuth(V) and antimony(V) compounds [Ph3Pn] stabilized by Lewis bases. These structures show trigonal bipyramidal geometry in which two individual Lewis bases as O=PPh3 or DMAP are in apical position and phenyl groups are in equatorial. The introduction of bidentate-type bipyridine ligand gave [Ph3Sb(bipy)OTf]OTf, which interestingly has a distorted octahedral structure. Their application in catalysis will be examined, Burford mentions.
-
References
[1] “Green bismuth”
Mohan, Ram. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 336. DOI: 10.1038/nchem.609
Bismuth is a remarkable eco-friendly metal with numerous applications in everyday life. With increasing awareness for the environment, one can expect to see a rise in the use of green metals such as bismuth in applications ranging from organic synthesis to engineering.
-
Related Products
[amazonjs asin=”B008MB1MCE” locale=”US” title=”Bismuth Crystal”][amazonjs asin=”B00FS2O3E4″ locale=”JP” title=”Bismuth-Containing Compounds (Springer Series in Materials Science)”]
-
Related Links
Burford Lab home Page