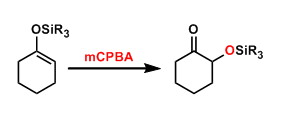
General Characteristics The epoxidation of silyl enol ethers with oxidants such as mCPBA and dioxirane leads to rearrangement into α-silyloxyketones. This reaction is used commonly to introduce a ...
Posts by Category: Reactions
Oxidation with Dioxiranes
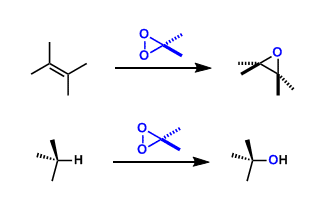
General Characteristics Dimethyldioxirane (DMDO), prepared from acetone and Oxone®, is used frequently to oxidize alkenes to epoxides. Methyl(trifluoromethyl)dioxirane (TFDO) is about 600 times more ...
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
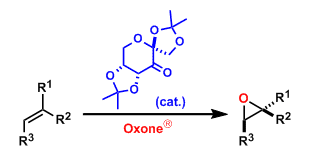
General Characteristics The asymmetric epoxidation of alkenes using the in situ generated chiral dioxirane formed from the fructose-derived ketone pre-catalyst and Oxone® (potassium ...
Oxidative Coupling of Enolates
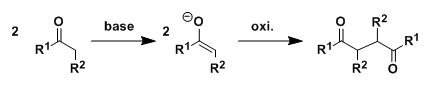
General Characteristics Enolate species undergo dimerization under appropriately chosen oxidative conditions. Homo-coupling usually predominates, but there are successful examples of controlled ...
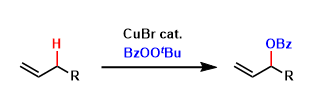
Kharasch-Sosnovsky Oxidation
General Characteristics Allylic C-H oxidation can be effected using acylperoxide under copper-catalyzed conditions. The alkene starting materials are usually used in excess. The terminal olefins are ...
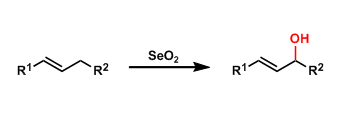
Selenium Dioxide
General Characteristics Selenium dioxide oxidizes allylic C-H bonds, providing an option to synthesize allylic alcohols from alkenes. Even though SeO2 is a toxic reagent, it is used frequently since ...
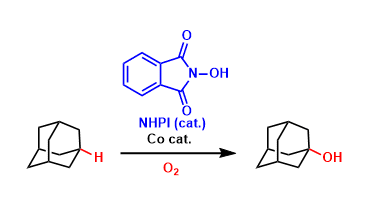
C-H Oxidation with NHPI Catalyst
General Characteristics An organocatalyst N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) forms the strongly oxidizing N-oxyl radical species (PINO) in the presence of appropriate oxidizing agents. This radical is ...
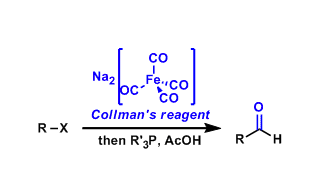
Collman’s Reagent
General Characteristics Disodium tetracarbonylferrate is generally referred to as the Collman reagent. It reacts with alkyl halides to give corresponding aldehydes and ketones. General References ...
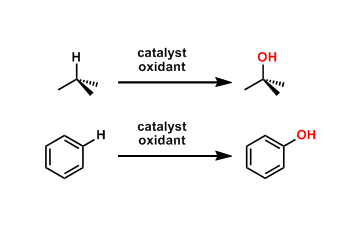
Catalytic C-H Oxidation
General Characteristics Catalytic C-H oxidation is a type of C-H activation reactions by which one can oxygenate unreactive C-H bonds, which are present ubiquitously in organic compounds. The C-H ...
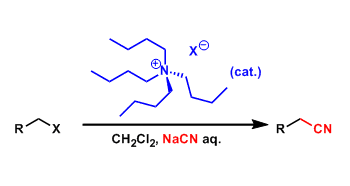
Phase-Transfer Catalyst (PTC)
General Characteristics Reactions such as SN2 substitution involve deprotonation by strong bases and combining the resulting anions with electrophiles. These reactions often necessitate the use of ...