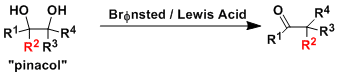
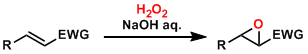General Characteristics Vicinal diol compounds (pinacols) undergo dehydrative rarrangement under strongly acidic conditions to produce carbonyl compounds. Since alkyl, aryl, and hydride are all ...
Posts by Category: Reactions
Claisen Condensation
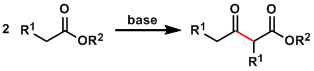
General Characteristics The base-promoted condensation of esters is called the Claisen condensation. The crossed-Claisen condensation between two different esters is effective if one of the esters ...
Nucleophilic Epoxidation with Peroxides
General Characteristics Electron-deficient olefins are epoxidized by oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide and t-butylhydroperoxide (TBHP) under basic conditions. Olefins without electron-withdrawing ...
Miyaura-Ishiyama-Hartwig Borylation
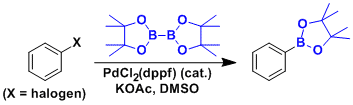
General Characteristics Synthetically important aryl and alkenyl boron compounds can be synthesized from the corresponding halides via transition metal catalysis. Bis(pinacolato)diboron is used ...
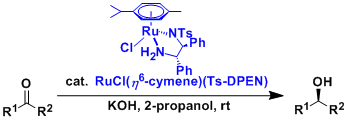
Noyori Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation
General Characteristics The asymmetric “transfer hydrogenation” of ketones is catalyzed by Ru(II)-arene-tosyldiamine and related complexes. Some of these ruthenium complexes are commercially ...
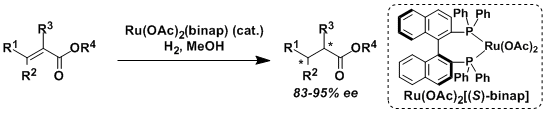
Noyori Asymmetric Hydrogenation
General Characteristics The asymmetric hydrogenation of olefins and ketones catalyzed by Ru(II)-BINAP and related ruthenium complexes is called the Noyori hydrogenation. The hydrogenation of olefins ...
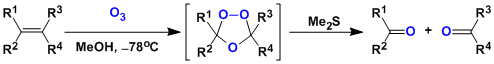
Harries Ozonolysis
General Characteristics Ozonolysis is a reaction between alkenes and ozone, in which the alkenes are cleaved into a pair of carbonyl compounds. The reaction is done by introducing ozone gas ...
Cannizzaro Reaction
General Characteristics Upon treatment with strong bases (e.g. in aqueous NaOH) and heating, non-enolizable aldehydes undergo redox disproportionation to give corresponding alcohols and carboxylic ...
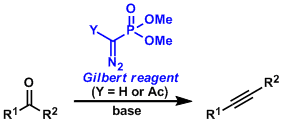
Seyferth-Gilbert Alkyne Synthesis
General Characteristics Aldehydes and ketones can be converted into alkynes with one carbon homologation using the α-diazophosphonate compound called the Gilbert reagent. When Y=H, the reaction needs ...
Clemmensen Reduction
General Characteristics The Clemmensen reduction is the reductive conversion of carbonyl groups into corresponding methylene units using zinc amalgam-HCl, which works particularly well for the ...