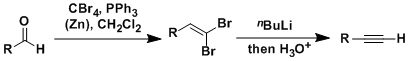
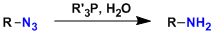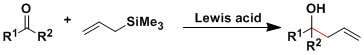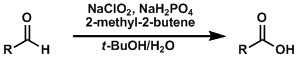General Characteristics The Corey-Fuchs reaction is the conversion of aldehydes into alkynes with one carbon homologation. The treatment of 1,1-dihaloalkenes with 2 equivalents of alkyllithium gives ...
Posts by Category: Reactions
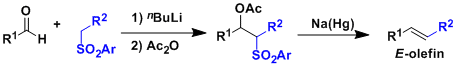
Julia-Lythgoe Olefination
General Characteristics The Julia-Lythgoe olefination involves the nucleophilic addition of lithiosulfones to carbonyl compounds, acylation, and reductive treatment of the resulting ...
Staudinger Reaction
General Characteristics In the Staudinger reaction, azide compounds react with phosphines to form iminophosphorane species, which can be hydrolyzed to give primary amines. The iminophosphorane also ...
Hosomi-Sakurai Allylation
General Characteristics The allylation reactions using allylsilanes are known as the Hosomi-Sakurai allylation. Allylsilanes are less toxic than allylstannanes and more stable than allyl Grignard and ...
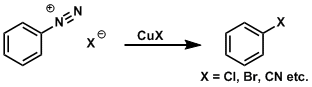
Sandmeyer Reaction
General Characteristics The transformation of aromatic diazonium compounds is known as the Sandmeyer reaction. Diazonium compounds are readily prepared from precursors such as nitro and aniline ...
Fukuyama Indole Synthesis
General Characteristics The Fukuyama indole synthesis is a powerful way to synthesize 3-substituted or 2,3-disubstituted indoles using a radical initiator and tributyltin hydride. The second ...
Tamao-Fleming Oxidation
General Characteristics Organosilicon compounds containing hetero atom substituent(s) on the silicon atom are oxidized by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a fluoride source and a weak base. The ...
Osmium Tetroxide (OsO4)
General Characteristics In the presence of re-oxidants, a catalytic amount of osmium tetroxide (OsO4) converts alkenes into cis-vicinal diols. Because of the mild reaction conditions and shortage of ...
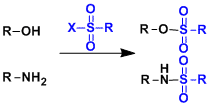
Sulfonyl Protective Groups
General Characteristics Sulfonyl groups are stable under both acidic and basic conditions. They are also used for purposes other than protection. Commonly used groups are methanesulfonyl (Ms), ...
Pinnick (Kraus) Oxidation
General Characteristics The Pinnick (or Kraus) oxidation reaction converts aldehydes into carboxylic acids under especially mild conditions. The Jones oxidation, PDC, ruthenium tetroxide, etc. are ...