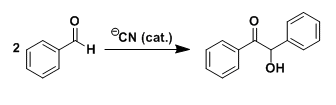
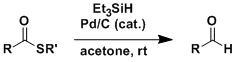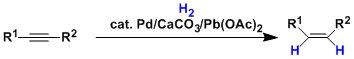General Characteristics In the presence of nucleophilic catalysts such as cyanide, aromatic aldehydes dimerize to form products called benzoins. Benzoin derivatives are important intermediates for ...
Posts by Category: Reactions
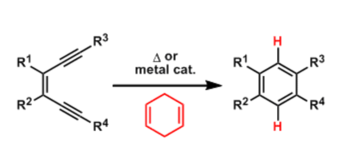
Masamune-Bergman Reaction
General Characteristics When heated at above 200 °C, cis-1,5-hexadiyne-3-ene cyclizes to form 1,4-benzene biradical. The highly reactive biradical species becomes benzene in the presence of hydrogen ...
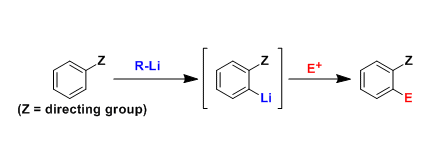
Directed Ortho Metalation
General Characteristics Ortho-selective functionalization of aromatic compounds is possible for the substrates having appropriate directing atoms or groups. Directed ortho metalation (abbreviated as ...
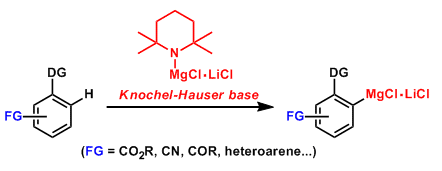
Knochel-Hauser Base
General Characteristics TMPMgCl-LiCl is known as the Knochel-Hauser base and a useful reagent for directed metalation of aromatic compounds. The metalation of aromatic compounds are conventionally ...
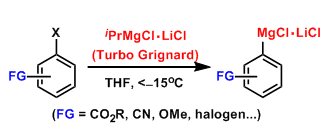
Turbo Grignard Reagent
General Characteristics The addition of one equivalent of lithium chloride when preparing Grignard reagents accelerates both the metal-halogen exchange and the insertion of magnesium. RMgCl-LiCl is ...
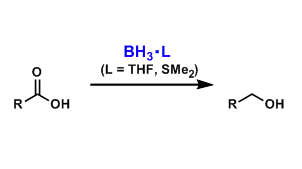
Borane Complexes (BH3・L)
General Characteristics Uncomplexed borane (BH3), which usually exists as diborane (B2H6), is difficult to handle since it is a toxic and pyrophoric gas. When complexed with THF or dimethylsulfide, ...
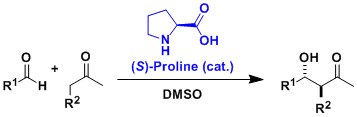
List-Barbas Aldol Reaction
General Characteristics The asymmetric aldol reactions can be catalyzed by simple amino acids such as proline. The proline-catalyzed intramolecular asymmetric aldol reactions of limited substrates ...
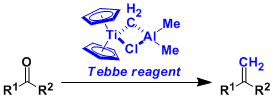
Tebbe Reagent
General Characteristics The titanium-based Tebbe reagent is a valuable tool when converting carbonyl groups into exo-olefins. The reagent can be used for the methylenation of not only aldehydes and ...
Fukuyama Reduction
General Characteristics Thioesters can be converted into aldehydes directly without going through complete reduction to alcohols. By the Fukuyama procedure, the reduction can be effected under very ...
Lindlar Reduction
General Characteristics The palladium catalyst supported on calcium carbonate and partially deactivated (“poisoned”) with lead acetate and quinoline is called the Lindlar catalyst. Using the Lindlar ...