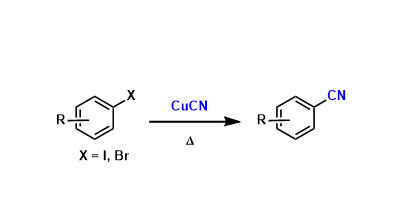
General Characteristics Aromatic nitriles can be synthesized from the corresponding aryl halides using copper(I) cyanide. The reaction tends to require high temperature conditions but is ...
Posts by Category: Reactions
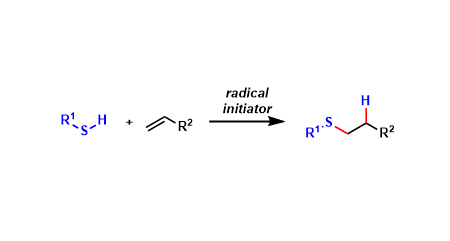
Thiol-ene Reaction
General Characteristics Thiols and alkenes undergo free-radical mediated S-C bond formation known as thiol-ene reaction. Thanks to its high chemoselectivity and functional group tolerance, it is ...
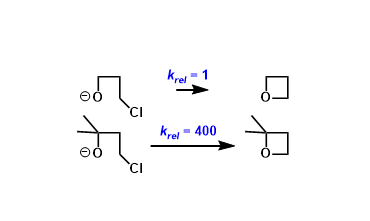
Thorpe-Ingold Effect
General Characteristics The effect of geminal substitution in linear molecules that promotes cyclization is referred to as the Thorpe-Ingold effect (aka. gem-dialkyl effect). General References ...
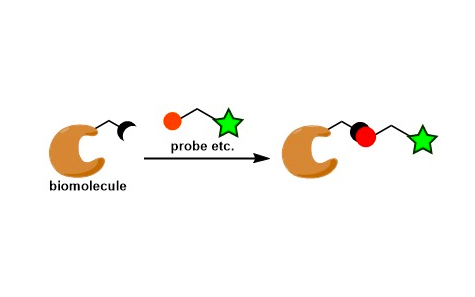
Bioconjugation
General Characteristics Bioconjugation is a process of covalently functionalizing biological molecules. It is most relevant to protein chemistry and is one of the newest topics in reaction ...
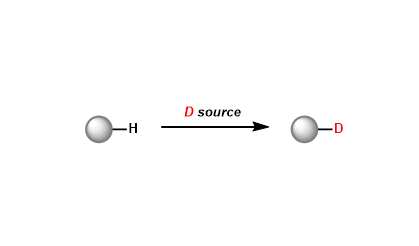
Deuterium Labeling Reaction
General Characteristics The exchange of hydrogen with its isotope deuterium has a wide range of useful applications. The underlying principle is that while replacement of hydrogen with deuterium ...
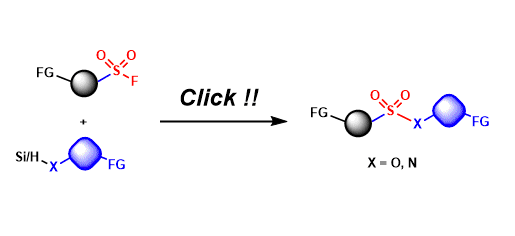
Sulfur(VI)-Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)
General Characteristics Sulfur(VI) fluoride compounds (e.g. RSO2F, SO2F2) are stable under a wide range of conditions, yet their S-F bonds can be activated for exchange reactions in the presence of ...
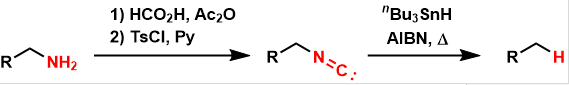
Barton Deamination
General Characteristics In the Barton deamination, amines are converted to isonitriles and then reductively removed under free-radical conditions, yielding simple hydrocarbons. General References ...
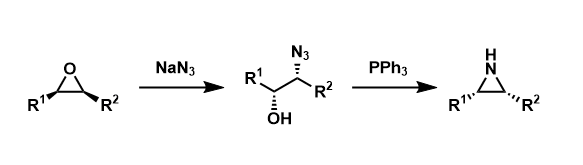
Blum-Ittah Aziridine Synthesis
General Characteristics Epoxides can be converted into aziridines by nucleophilic attack of azide ion, the Staudinger reaction, and aziridine ring formation with elimination of triphenylphosphine ...
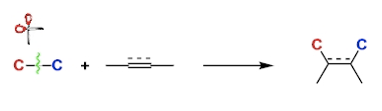
C-C Bond Activation
General Characteristics Carbon-carbon bonds are among the strongest in organic compounds. Activating them for useful chemical transformation is one of the newest and biggest challenges in organic ...
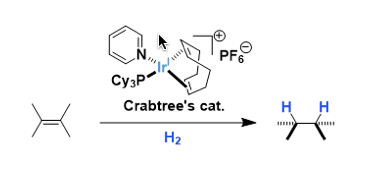
Crabtree’s Catalyst
General Characteristics [Ir(cod)(PCy3)(Py)]PF6 is an easily handleable cationic iridium complex used as a homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst. The complex was developed by Robert Crabtree of Yale ...