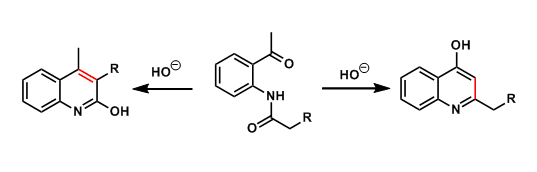
General Characteristics The basic treatment of ortho-acylaminoacetophenones leads to cyclocondensation, producing hydroxyquinolines. The experimenter needs to be aware of possible isomer formation. ...
Posts by Category: Reactions
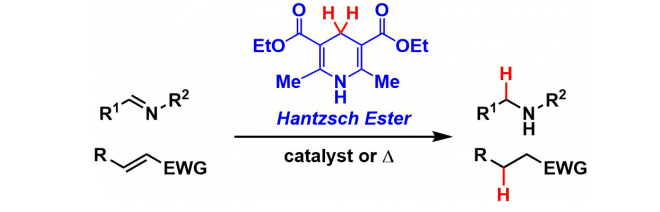
Transfer Hydrogenation with Hantzsch Ester
General Characteristics Dihydropyridine (Diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate) synthesized from formaldehyde and ethyl acetoacetate is commonly called the Hantzsch ester. The ...
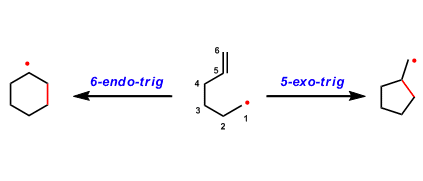
Baldwin’s Rule
General Characteristics The rate of ring closing reactions is largely influenced by how easily the orbitals can interact and overlap at the reacting parts of the molecule. The empirical rule that ...
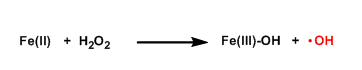
Fenton Reaction
General Characteristics The hydroxyl radical generated from H2O2 in the presence of iron(II) is used to promote various decomposition reactions. Copper(I) is known to have a similar property as well. ...
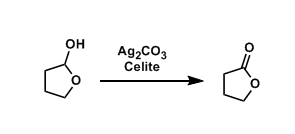
Fetizon’s Reagent
General Characteristics Silver(I) carbonate supported on Celite is called the Fetizon’s reagent. It is a mild oxidizing agent and particularly useful for the oxidation of lactols to lactones. ...
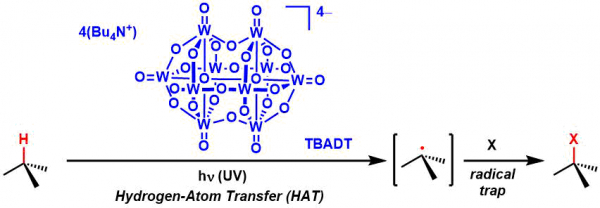
Tungstate Photocatalyst
General Characteristics Tetrakis(tetrabutylammonium) decatungstate (TBADT) is an organic solvent-soluble polyoxometalate compound that can act as a C-H abstraction catalyst under UV-activated ...
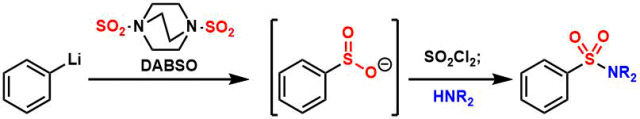
SO2 Incorporation Using DABSO
General Characteristics Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a synthetically useful reagent as a source of sulfur but it has to be used with care in a well-ventilated hood since it is a toxic gas. DABSO, the ...
Eschenmoser Coupling
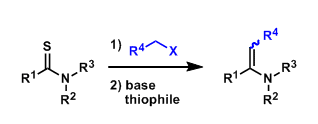
General Characteristics The Eschenmoser coupling begins with the S-alkylation of thioamides and gives enamine products (vinylogous amides, urethanes, etc.). As shown below, thiophiles (e.g. ...
Duff Reaction
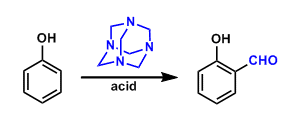
General Characteristics The formylation of phenols and anilines using hexamethylenetetramine is known as the Duff reaction. General References Duff, J. C.; Bills, E. J. J. Chem. Soc. 1932, 1987; ...