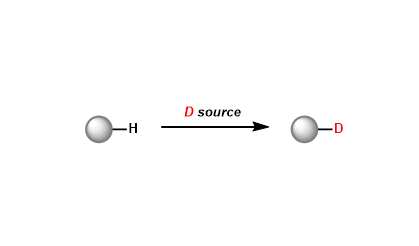
General Characteristics The exchange of hydrogen with its isotope deuterium has a wide range of useful applications. The underlying principle is that while replacement of hydrogen with deuterium ...
Author Archive
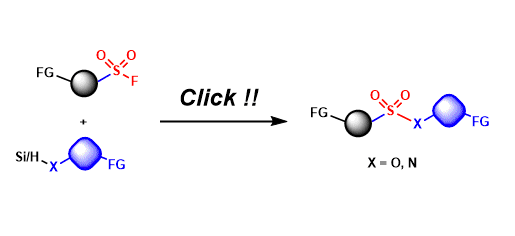
Sulfur(VI)-Fluoride Exchange (SuFEx)
General Characteristics Sulfur(VI) fluoride compounds (e.g. RSO2F, SO2F2) are stable under a wide range of conditions, yet their S-F bonds can be activated for exchange reactions in the presence of ...
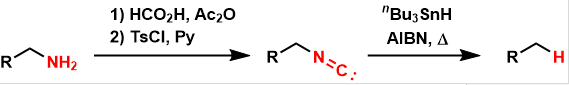
Barton Deamination
General Characteristics In the Barton deamination, amines are converted to isonitriles and then reductively removed under free-radical conditions, yielding simple hydrocarbons. General References ...
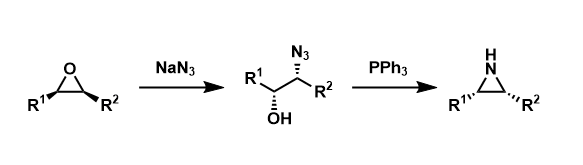
Blum-Ittah Aziridine Synthesis
General Characteristics Epoxides can be converted into aziridines by nucleophilic attack of azide ion, the Staudinger reaction, and aziridine ring formation with elimination of triphenylphosphine ...
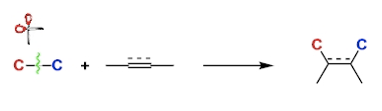
C-C Bond Activation
General Characteristics Carbon-carbon bonds are among the strongest in organic compounds. Activating them for useful chemical transformation is one of the newest and biggest challenges in organic ...
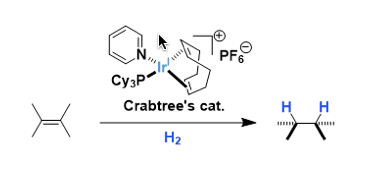
Crabtree’s Catalyst
General Characteristics [Ir(cod)(PCy3)(Py)]PF6 is an easily handleable cationic iridium complex used as a homogeneous hydrogenation catalyst. The complex was developed by Robert Crabtree of Yale ...
Giese Radical Addition
General Characteristics Carbon free-radicals (generated from organic halides, the Barton esters, etc.) are nucleophilic and can be trapped with various electrophiles. In particular, trapping of ...
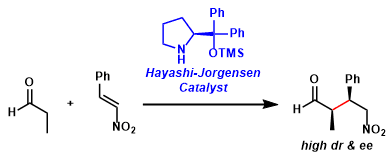
Hayashi-Jørgensen Catalyst
General Characteristics The diarylprolinol silyl ether organocatalysts facilitate various asymmetric reactions of aldehydes by forming active enamine and/or iminium intermediates. These catalysts are ...
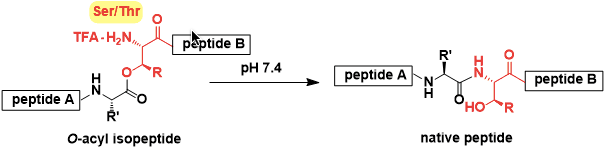
O-Acylisopeptide Method
General Characteristics The peptides in which the serine and/or threonine residues are isomerized from amide to ester (with their side chain hydroxyl group) are called O-acylisopeptides. ...
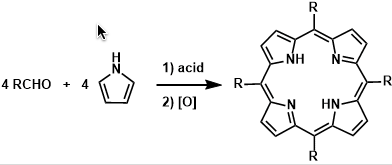
Rothemund-Lindsey Porphyrin Synthesis
General Characteristics Meso-substituted porphyrins are synthesized by condensation of aldehydes and pyrroles followed by oxidation. The early methods needed forcing conditions but the improvements ...