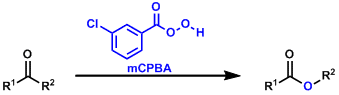
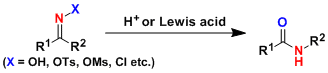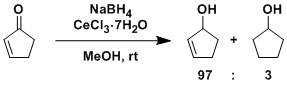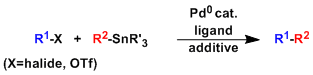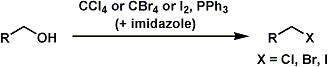General Characteristics -The conversion of ketones into esters by oxidation using peracids is called the Baeyer-Villiger reaction. In unsymmetrical ketones, the more substituted (the more ...
Author Archive
Beckmann Rearrangement
General Characteristics -The Beckmann rearrangement is the acid-induced rearrangement of oximes or its derivatives, which after hydration and tautomerization produces amides. Cyclic oximes give ...
Luche Reduction
General Characteristics -While 1,4-reduction usually predominates in the reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones with NaBH4 alone, selective 1,2-reduction is possible using CeCl3-7H2O as an additive. ...
Migita-Kosugi-Stille Cross Coupling Reaction
General Characteristics -The palladium-catalyzed cross coupling of organic halides or triflates with organotin compounds is known as the Migita-Kosugi-Stille coupling. -The reaction works under very ...
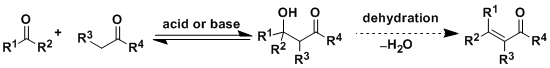
Classical Aldol Reaction
General Characteristics -In aldol reactions, the enol or the enolate of a ketone attacks an aldehyde or another ketone to generate a β-hydroxyketone (“aldol”). In the most classical procedure, the ...
Appel Reaction
General Characteristics The Appel reaction converts primary and secondary alcohols into corresponding alkyl halides. The reaction is suitable for both acid- and base-sensitive alcohols since the ...
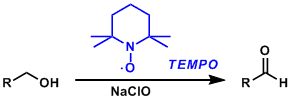
TEMPO Oxidation
General Characteristics 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl radical (TEMPO) is a stable and commercially available organic free radical reagent used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes. It is ...
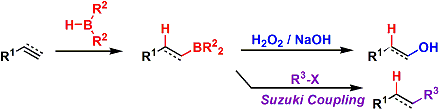
Brown Hydroboration
General Characteristics -Alkenes can be converted into anti-Markovnikov alcohols by the Brown hydroboration, which involves regio/stereoselective syn-addition of a B-H bond to the olefin followed by ...
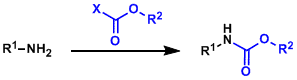
Carbamate Protective Groups
General Characteristics In order to tame the basicity and the high reactivity of amines during multi-step synthesis, it is common to protect them with electron-withdrawing functional groups. ...
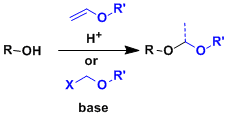
Acetal Protective Groups
General Characteristics Alcohols can be protected as acetals against reductive and basic conditions. Oxygen-based acetals are also stable under oxidizing conditions. Deprotection is usually done ...