Helmy, S.; Leibfarth, F. A.; Oh, S.; Poelma, J. E.; Hawker, C. J .; de Alaniz, J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8169–8172
DOI: 10.1021/ja503016b
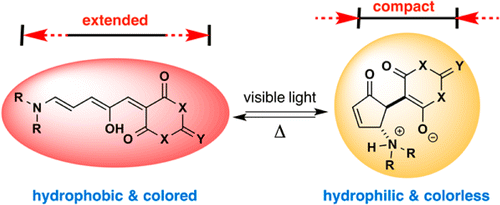
A versatile new class of organic photochromic molecules that offers an unprecedented combi- nation of physical properties including tunable photo-switching using visible light, excellent fatigue resistance, and large polarity changes is described. These unique features offer significant opportunities in diverse fields ranging from biosensors to targeted delivery systems while also allowing non-experts ready synthetic access to these materials.
A versatile new class of organic photo-chromic molecules that offers an unprecedented combination of physical properties including tunable photo-switching using visible light, excellent fatigue resistance, and large polarity changes is described. These unique features offer significant opportunities in diverse fields ranging from biosensors to targeted delivery systems while also allowing non-experts ready synthetic access to these materials.
In this paper, a new class type of photochromic compound was reported.
Unlike other existing organic photochromic compound, the newly prepared dyes possess some new properties.
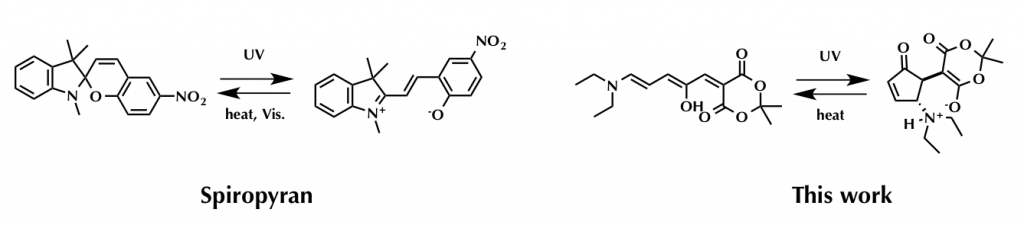
(1) Photochromic reaction, the structural change upon light exposure, entails the generation of cation and anion charge which is often seen in spiropiran derivatives[1].
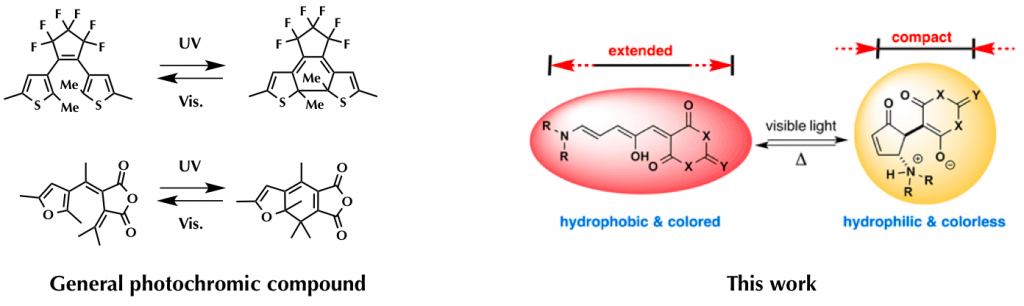
(2) The conformational changes between both isomer are extremely large compared to that of other existing photochromic compounds like diarylethene and fulgide.
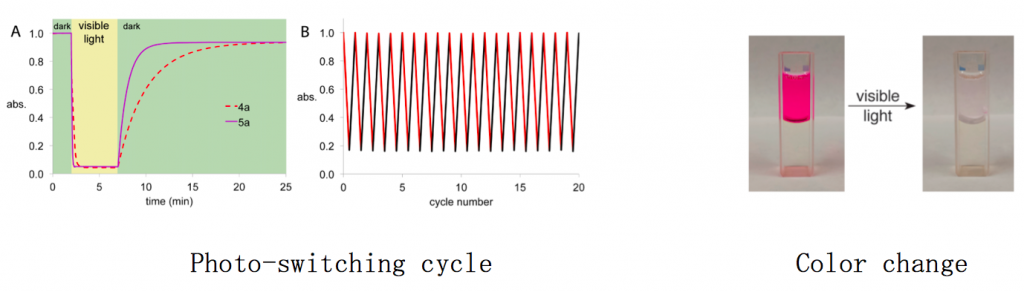
(3) The photochromic reaction can be modulated by alternate irradiation of long wavelength visible light and thermal reaction of room temperature. In other word, the photochromic reaction undergoes without using UV-light which is toxic and lethal for organic compound.
In addition to these unique properties, these dyes have relatively strong photo-resistance, absorption maximum in long wavelength region, and good PSS(photostationary state) conversion rate between both isomers.
Considering the further application in material devise and biology, the photochromic reaction efficiency(quantum yield of the reaction) have to be accelerated.
- Reference
(1) Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, Vol. 41, No. 3, 2005
(2) “Photo-responsive systems and biomaterials: photochromic polymers, light-triggered self-assembly, surface modification, fluorescence modulation and beyond”
Polym. Chem., 2010,1, 37-54 DOI: 10.1039/B9PY00300B
There has been considerable interest in the application of photochromism to photo-responsive systems which has led to the development of new tailored smart materials for photonics and biomedical fields. Within a polymeric matrix photochromic isomerizations can be stimulated by light to reversibly alter the physical and chemical properties of a material such as LC phase, shape, surface wettability, permeability, solubility, self-assembly, size and fluorescence. The underlying principles behind photo-responsive behavior, subsequent applications and relevant examples are discussed in this review.