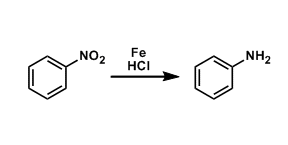
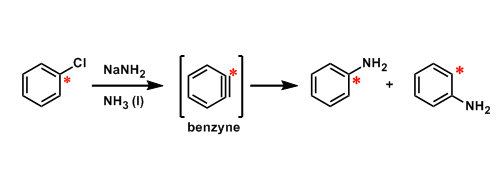
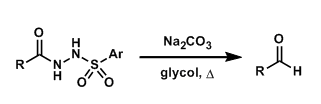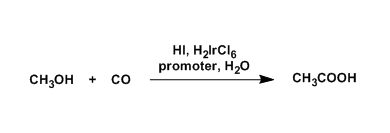General Characteristics The reduction of aromatic nitro group using iron powder and HCl is called the Bechamp reduction. Besides these classical conditions, other reagents such as tin(II) chloride ...
Monthly Archives: May 2017
McFadyen-Stevens Reaction
General Characteristics The thermal decomposition of acylarylsulfonylhydrazines into the corresponding aldehydes under basic conditions is known as the McFadyen-Stevens reaction. The reaction has ...
Kolbe Electrolysis
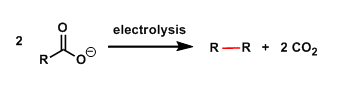
General Characteristics The decarboxylation of carboxylic acids and dimerization of the R group under electrolytic conditions is known as the Kolbe electrolysis. General References Kolbe, H. Ann. ...
Hinsberg Oxindole Synthesis
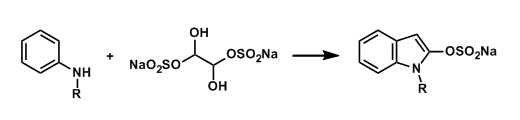
General Characteristics 2-Oxygenated indoles can be synthesized from the corresponding secondary aryl amines and bisulfite adduct of glyoxal. General References Hinsberg, O. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. ...
Monsanto Process for Acetic Acid Synthesis
General Characteristics Monsanto developed an industrial scale process for manufacturing acetic acid. In this process, the rhodium complex and cocatalytic hydroiodic acid catalyzes the carbonylation ...
Cativa Process for Acetic Acid Synthesis
General Characteristics Acetic acid is produced in different ways, such as by carbonylation of methanol and oxidation of acetaldehyde or hydrocarbons. The two carbonylation processes, the ...
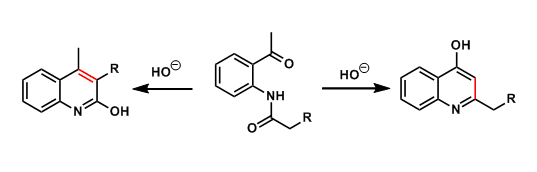
Camps Quinoline Synthesis
General Characteristics The basic treatment of ortho-acylaminoacetophenones leads to cyclocondensation, producing hydroxyquinolines. The experimenter needs to be aware of possible isomer formation. ...
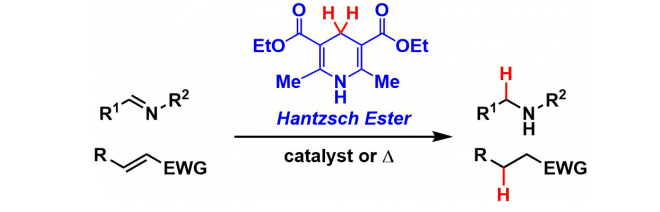
Transfer Hydrogenation with Hantzsch Ester
General Characteristics Dihydropyridine (Diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate) synthesized from formaldehyde and ethyl acetoacetate is commonly called the Hantzsch ester. The ...
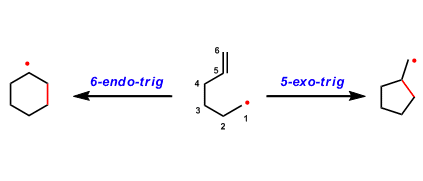
Baldwin’s Rule
General Characteristics The rate of ring closing reactions is largely influenced by how easily the orbitals can interact and overlap at the reacting parts of the molecule. The empirical rule that ...