- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
-
General Characteristics
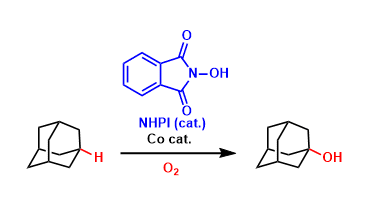
An organocatalyst N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) forms the strongly oxidizing N-oxyl radical species (PINO) in the presence of appropriate oxidizing agents. This radical is highly active in abstracting a hydrogen from hydrocarbons.
This is a valuable catalytic system in which C(sp3)-H bonds can be oxidized under relatively mild conditions. Further developments, especially the improvement of regioselectivity, are awaited.
-
General References
- Ishii, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Takeno, M.; Sakaguchi, S.; Iwahama, T.; Nishiyama, Y. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 3934. DOI: 10.1021/jo00118a002
<reviews>
- Ishii, Y.; Sakaguchi, S.; Iwahama, T. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2001, 343, 393. [abstract]
- 石井康敬、有機合成化学協会誌 2001, 59, 2. [PDF]
- Recupero, F.; Punta, C. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3800. DOI: 10.1021/cr040170k
- Melone, L.; Punta, C. Beil. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1296. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.9.146
-
Reaction Mechanism

-
Examples
In recent years, the NHPI system has been extended to the direct fluorination[1] and amination[2] of sp3 C-H bonds.


-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] Amaoka, Y.; Nagatomo, M.; Inoue, M. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2160. DOI: 10.1021/ol4006757
[2] Amaoka, Y.; Kamijo, S.; Hoshikawa, T.; Inoue, M. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 9959. DOI: 10.1021/jo301840e
-
Related Reactions
-
Related Books
-
External Links
N-Oxy Radical Chemistry (The Kanai Group at University of Tokyo, PDF)