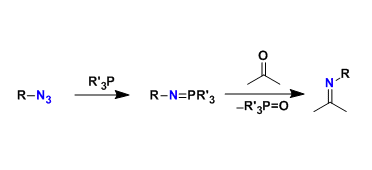- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
- Application to Chemical Biology
-
General Characteristics
Nucleophilic phosphorus reagents such as triphenylphosphine react with azides to generate, via the Staudinger reaction, N-P ylide (iminophosphorane) intermediates, which react with carbonyl compounds to produce imines. Therefore, this reaction is considered the nitrogen version of the Wittig reaction.
-
General References
Shah, S.;Protasiewicz,J. D. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 210, 181. doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(00)00311-8
Palacios, F.; Alonso, C.; Aparicio, D.; Rubiales, G; M. de los Santos, J. M. Tetrahedron, 2007, 63, 523. DOI: 10.1016/j.tet.2006.09.048
-
History
In 1919, Staudinger and Myers reported that azides and phosphines reacted to form N-P ylides, which could be converted to amines after hydrolysis (the Staudinger reaction). About 30 years later, it was demonstrated that the N-P ylides could react with carbonyl compounds to give imines. This and related reactions are called the aza-Wittig reaction.
-
Reaction Mechanism

-
Examples
Iminophosphoranes can react with a variety of electrophiles to give the corresponding products, as summarized below.

An application to the synthesis of a secondary amine.

-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
-
Related Reactions
Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons (HWE) Reaction
-
Related Books
-
External Links
Bertozzi ResearchGroup (UC Berkeley)
A New way to Engineer Cells: The Staudinger Ligation: Chemoselective, mild, and high-yielding chemical ligation based on the Staudinger reaction.