- Generality
- Reagent Availability
- Experimental User Friendliness
-
General Characteristics
-The synthesis of unsymmetrical ethers by SN2 displacement of alkyl halides by alkoxides is called the Williamson ether synthesis. The reaction works best when the R group is primary.
-In certain cases such as trityl protection, the reaction proceeds by SN1 pathway.
–E2 elimination is the main competing reaction, which predominates for tertiary alkyl halides.
-SN2-promoting aprotic polar solvents such as acetonitrile and DMF are generally used.
-The leaving group is not limited to halides. Alkyl sulfonates are equally usable.
-
General References
・Williamson, W. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1851, 77, 37.
・Williamson, W. J. Chem. Soc. 1852, 106, 229.
・Dermer, O. C. Chem. Rev. 1934, 14, 385. DOI: 10.1021/cr60049a002
-
Reaction Mechanism
-
Examples
In SNAr type reactions, note that the reactivity decreases in the order of F > Cl > Br > I.
![]()
-
Experimental Procedure
-
Experimental Tips
-
References
[1] J. R. Prous, ed. Drugs Fut. 1992, 17, 1093.
[2] J. R. Prous, ed. Drugs Fut. 2002, 27, 339.
[3] J. R. Prous, ed. Drugs Fut. 1990, 15, 1080.
-
Related Books

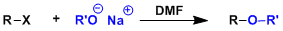
![williamson_3[1]](https://en.chem-station.com/wp-content/plugins/lazy-load/images/1x1.trans.gif)