Kitamura, K.; Ando, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Suzuki, K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013 Early View
DOI: 10.1002/ange.201308016
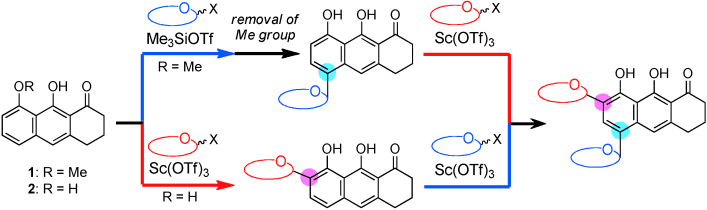
Two effective tricyclic platforms are reported for the installation of the two constituent sugars, l-vancosamine and d-angolosamine, in a regio- and stereoselective manner for the synthesis of the pluramycin class of bis-C-glycoside antitumor antibiotics. Two complementary protocols are now available that differ in the order in which the two sugar moieties are installed. Sc(OTf)3 was effective as the Lewis acid.
The pluramycin family of natural products are an important group of complex C-aryl glycoside antibiotics that possess the tetracyclic 4H-anthra[1,2-b]pyran-4,7,12-trione moiety A–D as an aromatic core. Prof. Keisuke Suzuki, Tokyo Institute of Technology has achieved a concise, highly convergent total synthesis of saptomycin B, a member of the pluramycin class of antitumor antibiotics.
The target compound was assembled from four building blocks (a tricyclic platform, two sugars, and an alkynal) in 15% yield through 10 synthetic operations (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201308017). The key steps included the regioselective installation of two amino sugars (l-vancosamine and d-angolosamine) on the tricycle and the efficient construction of the tetracyclic skeleton by an aldol reaction followed by formation of the pyranone. The unknown configuration at C14 was assigned as R
- Related Books